Industry Background
As a vital component and pillar of China's economy, the machining industry is primarily characterized by discrete manufacturing, supplemented by process-based production, with machining and assembly as its core focus. The industry encompasses a wide range of production processes, including casting, forging, stamping, welding, and assembly. With strong national policy support, the degree of automation and digitalization in the mechanical processing sector has improved. However, influenced by traditional production practices and legacy operating models—combined with intensifying market competition—traditional machining enterprises continue to face common challenges such as frequent and flexible changes in processes, planning, and equipment; highly customized products; weak inter-process connectivity; and a lack of effective quality monitoring. To stay competitive, companies must adopt lean manufacturing and pursue cost reduction and efficiency improvement as an inevitable path forward.
Management Challenges
The machining industry primarily operates based on customer orders, supplemented by demand forecasting. It is characterized by high product variety, fluctuating production volumes, strong customization requirements, a wide range of raw materials, long pre-production preparation and production cycles, and highly flexible process routes and equipment usage. As a result, enterprises face the following challenges in production management:
- Inaccurate production planning, poor executability, and low overall efficiency.
- Difficulty synchronizing resource information, leading to poor coordination and inadequate readiness before production.
- Frequent process changes that make it difficult to adjust and reschedule production plans in a timely manner, resulting in weak predictability.
- Lack of digital tools for warehouse and logistics management leads to poor timeliness of operations and low data accuracy.
- Inventory management functions are inadequate, line-side warehouse management is coarse, and logistics efficiency remains low.
- Long production flows make quality management difficult, and quality defects are hard to detect in a timely manner.
- The wide variety of equipment increases the difficulty of data acquisition, making preventive and proactive maintenance impossible.
- Equipment operates in isolated, stand-alone modes, without network connectivity for automated data collection and reporting.
- The production process lacks transparency, making it impossible to monitor and control production status in real time.
Solution
Designed for the specific needs of the machining industry, Morewis builds a lean-production–driven execution management platform that ensures accurate and efficiently transmitted production data. The solution covers core business modules including production planning and scheduling, process management, data acquisition, process control, product tracking, quality control, and equipment management. The system integrates seamlessly with ERP, enabling smooth data exchange across different systems. It collects, feeds back, and responds to shop-floor data in real time, while establishing standardized IT–OT interface protocols to fully digitalize the production process. By creating a unified management closed loop, the solution enables end-to-end transparency, digitalization, and intelligence across all elements of machining production—ultimately supporting enterprises in reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and improving quality.
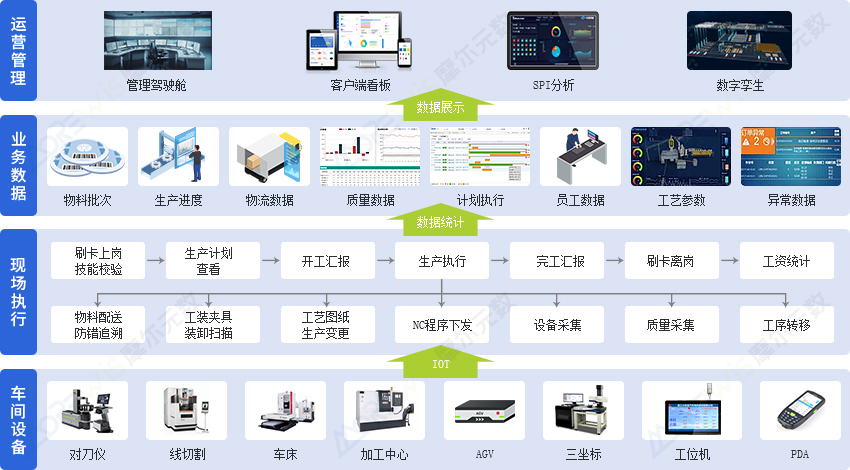
Business Blueprint for Digital Machining Solutions
Addressing Core Needs
- Establish and apply barcode-based management with multiple data acquisition methods to achieve source-level control.
- Conduct visualized collaborative planning and scheduling based on real-time material and subcontracting status, enabling production sequencing for work orders as well as task insertion, manual adjustments, and urgent order handling.
- Track production status, quality, process history, and logistics information through product serial numbers, material batch numbers, and other SN-related data.
- Configure flexible and user-friendly process flows, allowing operators to follow standardized workflow instructions and ensuring effective mistake-proofing.
- Collect real-time equipment data to enable remote monitoring and OEE performance analysis, build equipment asset records, and implement automated scheduled maintenance—achieving full equipment visibility.
- Effectively prevent material errors and omissions through barcode association and process-control analytics, enabling real-time computation, analysis, evaluation, and early warnings to achieve comprehensive quality management.
- Utilize workpiece identification technology to track every stage of order-based production, allowing dynamic, real-time visibility into the actual status of all operations within each task.
- Build a 4M-level traceability system using barcodes as the carrier and multiple data acquisition methods to ensure complete product traceability.
- Establish a multidimensional, efficient, and collaborative data analytics and decision-making platform that automatically generates visual production dashboards, monitors deviations between actual progress and plans in real time, and drives continuous production optimization.
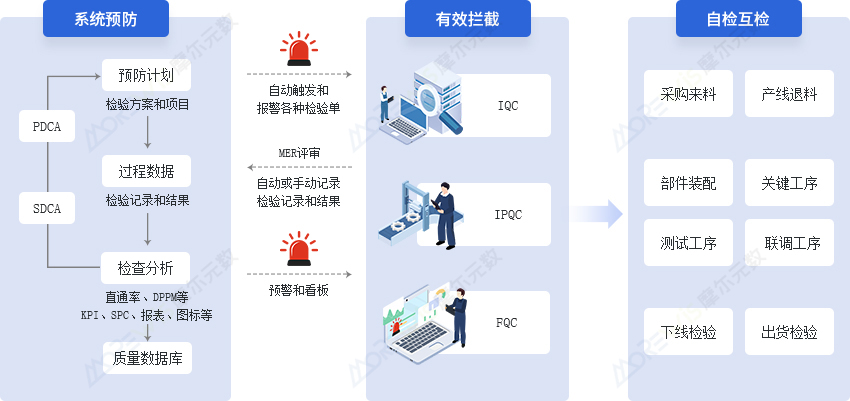
Transition from Coarse Management to Refined, Full-Value-Chain Quality Management
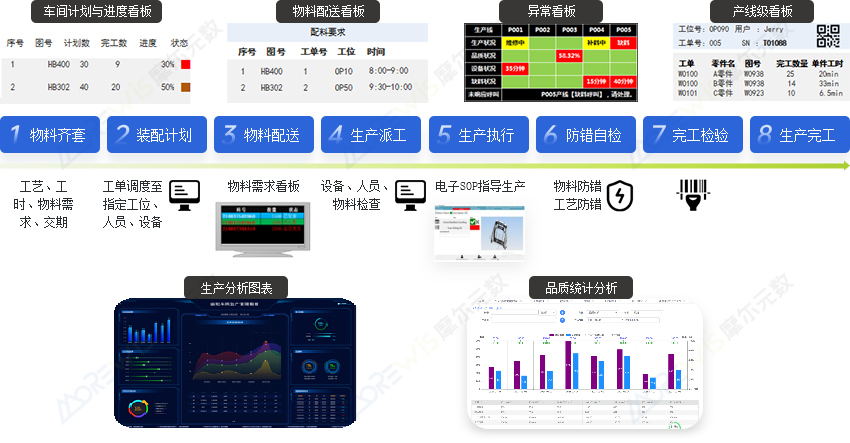
Machining Industry MES Application Scenarios

Machining Production Dashboard
Implementation Benefits
- Collect production data in real time to gain full visibility into production progress and achieve complete production transparency.
- Provide real-time, accurate production data to managers at all levels through event-triggered automatic data collection, enabling lean and informed decision-making.
- Capture detailed test data in real time to ensure comprehensive process-quality control and stabilize production processes.
- Analyze and track production information intelligently to continuously uncover equipment and operational potential, enhancing execution efficiency.
- Enable bidirectional quality traceability, supporting proactive planning, in-process control, and post-production analysis for lean management.